# Defining Algorithms and their Complexity
Table of Contents
Introduction
Describing what makes an algorithm can take many turns, the degrees in knowledge someone might understand is equivalent to their depth. But here I will try my best to define the primary features which make up algorithms, what their uses are, and what can be taken away from them.
This post will cover:
- What defines an algorithm and its essential characteristics
- Why algorithm efficiency matters in real-world applications
- How to measure and compare algorithm performance using Big O notation
- Common data structures and their relationship to algorithms
- Practical examples with detailed complexity analysis in C
What is an Algorithm?
(An algorithm is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions used to solve a type of specific problem or to perform a computation). While the definition for an algorithm can be broad, the focus on this blog is to tunnel on computer science data structures and why datasets are managed by them.
what does an algorithm do?
An algorithm takes a dataset and applies a fitting data structure to maximize efficiency.
Datasets can take many forms, however technically, all data structures can be defined as an array. With every index having alternative/unique methods to collect, distribute, and store each value held in memory. The choice of data structure directly impacts the efficiency of the algorithms that operate on the data.
A data structure is just a strategy for finding something in an array
- Nic Barker
Why Algorithms Matter
As a collection of data representing any form of stored data grows in size, machines/devices will require an exponential amount of computational power per increase to the quantity of data being accessed. Therefor using the appropriate algorithm for the right application, we’re cutting down the computational cost and simultaniously increasing speed/performance for accessing such dataset.
Computational Cost Problem
As an example lets take a database with 100 records and recursively scan all elements (records) to find the one you’re looking for. This wouldn’t be an issue for most databases as the speed which scanning 100 records for each element would take negligible time. But scanning each element for 1,000,000 records, checking 10,000 times more, could amount to over 10,000 times the work. However, an algorithm which uses the right data structure might only check 50 records to find the element being searched.
- Source Code to Execution
For each component, a compiler like gcc will convert that source code into Assembly with the C preprocessor. This is then converted into an object file .o by the assembler where gcc can link and match with the hardware and OS specifications of your machine to produce the final binary .exe file. Note that this is a complete oversimplification, but still may present a useful visual for understanding what goes into code execution.
see here for more info
gcc info
The purpose of quantitative measurements is to abstract computational clock cycles for each step of algorithmic recursion, defining an easier interpretation of what the machine code represents during execution.
Learning systems architecture and how bit manipulation can lead to marginally greater performance alongside algorithms is another topic that while holds relevancy for specific systems, will be outside the scope i’ll demonstrate. Here’s a good video explaining this bit manipulation: Why Some Low-Level Projects Are Full of Weird Code Like This
Understanding Algorithms
To analyze and compare algorithms objectively, we need to understand their fundamental properties and how to measure their performance.
Essential Characteristics
We must understand the terminology so that the collective information we have built from algorithms can be understood by many and applied realistically. To remain on the same page, we characterize algorithms by five defining features: Definiteness, Finiteness, Effectiveness, and Input/Output.
Characterising algorithms and defining their features; Definiteness, Finiteness, Effectiveness, and I/O, all come into what makes an algorithm.
Input: 0 or more
An algorithm can accept zero or more quantities as input, supplied externally before the algorithm begins.
Output: 1 or more
An algorithm must produce at least one output—a quantity that has a specified relation to the inputs.
Definiteness: Clear and unambiguous
Each instruction must be precisely defined with a definite value that terminates after method execution. There can be no ambiguity in the steps.
Finiteness: Terminates after finite steps
An algorithm must terminate after a finite number of steps. It should allow concurrency with other running programs / hold appropriate breakpoints.
Effectiveness: Serves its purpose
Every instruction must be sufficiently basic that it can be carried out in principle. The algorithm must serve a clear purpose in what’s being executed.
Measuring Algorithm Efficiency
Determining the effectiveness/necessity of an algorithm you will often consider these factors
Execution Time - How long an algorithm will take to run
Physical Space - Drive/Memory space an algorithm will take up
Network Usage - Quantity/Magnitude of transfers the algorithm takes up on a Network
CPU Registers - Clock Speed/Computational Efficiency for executing what’s been allocated
Power Consumption - Energy required for algorithm to perform most optimally
Time Complexity
Time Complexity is a measure of how an algorithm’s execution time grows relative to the size of its input. Rather than measuring actual seconds (which vary by hardware), time complexity counts the number of fundamental operations performed.
Time Complexity - The rate at which execution time increases as input size grows
Key points:
- Expressed as a function of input size (n)
- Counts operations, not clock time
- Independent of hardware, programming language, or implementation details
- Focuses on growth rate as input size increases
Time Function: A mathematical function representing the estimated number of operations an algorithm will perform based on input size.
Space Complexity
Space Complexity measures the total amount of memory space required by an algorithm relative to the input size.
Space Complexity - The amount of memory space required by an algorithm relative to input size
This includes:
Input space: memory to store the input data
Auxiliary space: extra memory used during computation (variables, temporary arrays, recursion stack)
Key considerations:
Some algorithms trade space for time (and vice versa)
Modern systems often have abundant memory, making time complexity more critical
Embedded systems and mobile devices still face memory constraints
Big O Notation
Big O notation uses mathematical notation to describe how well an algorithm performs as its input size grows. The runtime (time complexity) and memory space (space complexity) are measures to understand efficiency and capacity. An algorithm uses functions to understand when an argument (complexity) tends towards a certain value or infinity. In computer science, it typically describes the worst-case scenario for algorithm performance.
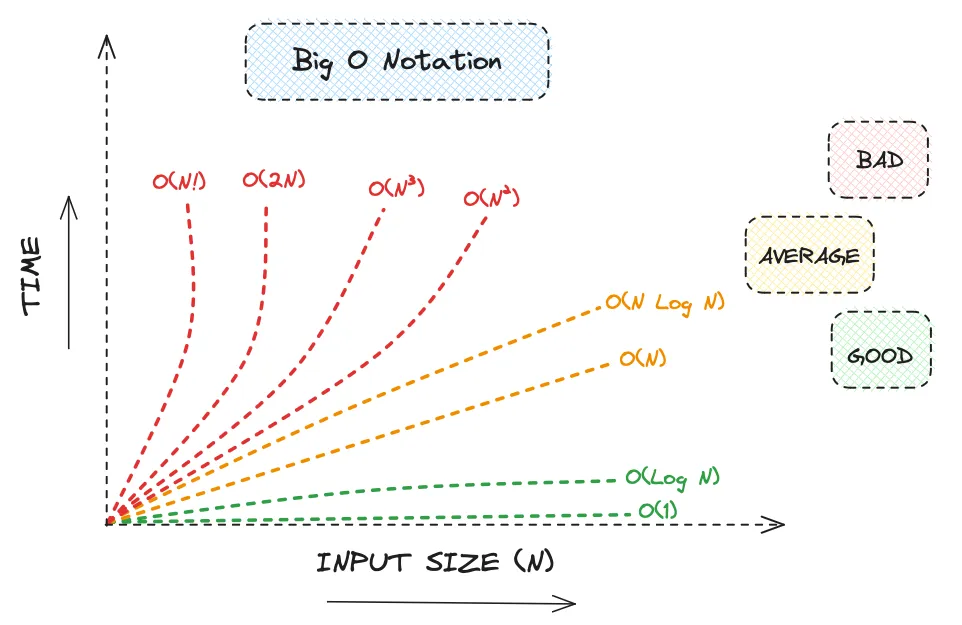
As N (the input size) grows larger, the best-case execution time becomes less meaningful because the worst-case often dominates runtime. Algorithms are designed to handle large input sizes, so accounting for worst-case scenarios is their primary purpose.
If a dataset is small enough that computation speed is adequate regardless of algorithm choice, then Big O analysis becomes less relevant. For this reason algorithms are dependant on relevancy, sorting an array with complexity can become less focused on algorithms and more on embedding.
Common Time Complexities
| Notation | Name | Example Operations | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | Array access | Doesn’t grow | |
| Logarithmic | Binary search | Very slow growth | |
| Linear | Linear search | Proportional to input | |
| Linearithmic | Quick sort | Faster than quadratic | |
| Quadratic | Bubble sort | Rapid growth | |
| Cubic | Matrix multiplication | Very rapid growth | |
| Exponential | Subset generation | Explosive growth | |
| Factorial | Generating all permutations | Extremely explosive |
When analyzing algorithms, we consider three scenarios:
-
Best Case (Ω - Omega): The minimum time/operations required
Example: Linear search finds the target at index 0 → O(1) -
Average Case (Θ - Theta): Expected performance over all possible inputs
Example: Linear search finds target in middle → O(n/2) = O(n) -
Worst Case (O - Big O): Maximum time/operations required
Example: Linear search doesn’t find target → O(n)
Algorithm Examples with Detailed Analysis
Demonstrating examples of algorithms applied using the C language with complete complexity analysis.
describe time and space complexity to distinguish differing algorithms.
Example 1: Basic Swap Algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
// Swap function using pointers// Space Complexity: O(1) - only uses one temporary variablevoid swap(int *x, int *y) /*1*/{ int temp; /*1 - allocates space for temp variable*/ temp = *x; /*1 - read value at x, store in temp*/ *x = *y; /*1 - read value at y, write to x*/ *y = temp; /*1 - read temp, write to y*/} /*Total time: 4 operations, Total space: 1 variable*/
// Main function// Overall Space Complexity: O(1) - fixed number of variablesint main() /*1*/{ int a; /*1 - allocates space for a*/ int b; /*1 - allocates space for b*/
a = 10; /*1 - assignment*/ b = 20; /*1 - assignment*/
printf("Before swap:\n"); /*1*/ printf("a = %d\n", a); /*1*/ printf("b = %d\n", b); /*1*/
swap(&a, &b); /*4 - function call executes 4 operations*/
printf("\nAfter swap:\n"); /*1*/ printf("a = %d\n", a); /*1*/ printf("b = %d\n", b); /*1*/
return 0; /*1*/}TIME COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS:
| Statement | Times Executed | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| int main() | 1 | O(1) |
| int a; | 1 | O(1) |
| int b; | 1 | O(1) |
| a = 10; | 1 | O(1) |
| b = 20; | 1 | O(1) |
| printf(“Before swap:\n”); | 1 | O(1) |
| printf(“a = %d\n”, a); | 1 | O(1) |
| printf(“b = %d\n”, b); | 1 | O(1) |
| swap(&a, &b); | 4 | O(1) |
| printf(“\nAfter swap:\n”); | 1 | O(1) |
| printf(“a = %d\n”, a); | 1 | O(1) |
| printf(“b = %d\n”, b); | 1 | O(1) |
| return 0; | 1 | O(1) |
| TOTAL | 16 | O(1) |
|---|
SPACE COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS:
| Variable/Memory | Space Units | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| int a (main) | 1 | O(1) |
| int b (main) | 1 | O(1) |
| int temp (swap) | 1 | O(1) |
| int *x (swap parameter) | 1 | O(1) |
| int *y (swap parameter) | 1 | O(1) |
| TOTAL | 5 | O(1) |
|---|
The swap algorithm uses a fixed number of operations and variables regardless of input. This is the hallmark of O(1) - constant time and space complexity.
Example 2: Merged Comparison of Multiple Algorithm Complexities
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdbool.h>
// Array Sum Result structtypedef struct { int sum; int size; int operations; // Track number of operations for complexity analysis} ArraySumResult;
// Linear Search Result structtypedef struct { bool found; int index; int size; int target; int comparisons; // Track comparisons for complexity analysis} LinearSearchResult;
// Bubble Sort Result structtypedef struct { int size; int comparisons; int swaps; int* sortedArray; // Pointer to sorted array} BubbleSortResult;
// Master struct for all algorithm resultstypedef struct { ArraySumResult sumResult; LinearSearchResult searchResult; BubbleSortResult sortResult;} AlgorithmResults;
// ARRAY SUM - O(n) Time, O(1) SpaceArraySumResult arraySum(int arr[], int n) /*1*/{ ArraySumResult result = {0, n, 0}; /*1 - initialize result struct*/ int i; /*1 - allocates space for loop counter*/
result.operations++; // Count initialization
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) /*n+1 - condition checked n+1 times*/ { result.sum += arr[i]; /*n - executed n times*/ result.operations++; // Count each addition }
return result; /*1*/}
// LINEAR SEARCH - O(n) Time, O(1) SpaceLinearSearchResult linearSearch(int arr[], int n, int target) /*1*/{ LinearSearchResult result = {false, -1, n, target, 0}; /*1 - initialize*/ int i; /*1 - allocates space for loop counter*/
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) /*best: 1, worst: n+1*/ { result.comparisons++; // Count each comparison if (arr[i] == target) /*best: 1, worst: n*/ { result.found = true; /*1*/ result.index = i; /*1*/ return result; /*1 - if found*/ } }
return result; /*1 - if not found*/}
// BUBBLE SORT - O(n²) Time, O(1) SpaceBubbleSortResult bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) /*1*/{ BubbleSortResult result = {n, 0, 0, arr}; /*1 - initialize result*/ int i; /*1 - outer loop counter*/ int j; /*1 - inner loop counter*/ int temp; /*1 - swap variable*/
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) /*n - outer loop*/ { for (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) /*n(n-1)/2 - inner loop*/ { result.comparisons++; // Count comparison if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) /*n(n-1)/2 comparisons*/ { // Swap elements temp = arr[j]; /*1*/ arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; /*1*/ arr[j + 1] = temp; /*1*/ result.swaps++; // Count swap (3 operations) } } }
return result; /*1*/}
// DATA GENERATION AND ALGORITHM EXECUTIONAlgorithmResults generateAlgorithmData() { // Define test array static int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90, 88, 45, 50}; int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int target = 22;
// Create master results structure AlgorithmResults results;
// Make a copy of array for sorting (to preserve original) static int sortArray[10]; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { sortArray[i] = arr[i]; }
// Execute all algorithms and store results results.sumResult = arraySum(arr, size); results.searchResult = linearSearch(arr, size, target); results.sortResult = bubbleSort(sortArray, size);
return results;}
// DISPLAY FUNCTIONS - print resultsvoid displayArraySumResult(ArraySumResult result) { printf("\n=== ARRAY SUM ALGORITHM ===\n"); printf("Array size: %d\n", result.size); printf("Sum: %d\n", result.sum); printf("Operations performed: %d\n", result.operations);}
void displayLinearSearchResult(LinearSearchResult result) { printf("\n=== LINEAR SEARCH ALGORITHM ===\n"); printf("Array size: %d\n", result.size); printf("Target value: %d\n", result.target);
if (result.found) { printf("Result: FOUND at index %d\n", result.index); } else { printf("Result: NOT FOUND\n"); }
printf("Comparisons made: %d\n", result.comparisons);}
void displayBubbleSortResult(BubbleSortResult result) { printf("\n=== BUBBLE SORT ALGORITHM ===\n"); printf("Array size: %d\n", result.size); printf("Comparisons made: %d\n", result.comparisons); printf("Swaps made: %d\n", result.swaps);
printf("Sorted array: "); for (int i = 0; i < result.size; i++) { printf("%d ", result.sortedArray[i]); } printf("\n");}
void displayResultsSummary(AlgorithmResults results) { printf("\n=======================================================================\n"); printf(" ALGORITHM RESULTS SUMMARY\n"); printf("=======================================================================\n"); printf("Algorithm | Result | Operations\n"); printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------\n"); printf("Array Sum | Sum = %-26d | %d\n", results.sumResult.sum, results.sumResult.operations); printf("Linear Search | %s | %d\n", results.searchResult.found ? "Found at index " : "Not found ", results.searchResult.comparisons); printf("Bubble Sort | Sorted successfully | %d\n", results.sortResult.comparisons + results.sortResult.swaps); printf("=======================================================================\n");}
int main() { // Generate and execute all algorithms AlgorithmResults results = generateAlgorithmData();
// Display individual results displayArraySumResult(results.sumResult); displayLinearSearchResult(results.searchResult); displayBubbleSortResult(results.sortResult);
// Display summary table displayResultsSummary(results);
printf("\n"); return 0;}
/*ALGORITHM 1: ARRAY SUM----------------------Time Complexity: O(n)- Single loop iterates n times- Each iteration: 1 addition operation- Total: n operations
Space Complexity: O(1)- Variables: sum, i, result struct- Space used doesn't grow with input size
ALGORITHM 2: LINEAR SEARCH---------------------------Time Complexity: O(n)- Best Case: O(1) - element at index 0- Average Case: O(n/2) = O(n) - element in middle- Worst Case: O(n) - element at end or not found
Space Complexity: O(1)- Variables: i, result struct- No additional space based on input
ALGORITHM 3: BUBBLE SORT-------------------------Time Complexity: O(n²)- Outer loop: n-1 iterations- Inner loop: decreasing from n-1 to 1- Total comparisons: (n-1) + (n-2) + ... + 1 = n(n-1)/2 ≈ n²/2- Swaps (worst case): up to n(n-1)/2 ≈ n²/2
Space Complexity: O(1)- Variables: i, j, temp, result struct- Sorts in-place, no extra array needed
GROWTH COMPARISON (for n=10):------------------------------Array Sum: ~10 operationsLinear Search: 1-10 operations (depends on position)Bubble Sort: ~45 comparisons + swaps
For n=20:Array Sum: ~20 operations (2x)Linear Search: 1-20 operations (2x)Bubble Sort: ~190 comparisons + swaps (4x) ← Quadratic growth*/ARRAY SUM - TIME COMPLEXITY:
| Statement | Times Executed | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| ArraySumResult result = {…}; | 1 | O(1) |
| int i; | 1 | O(1) |
| result.operations++; | 1 | O(1) |
| for (i = 0; i < n; i++) | n+1 | O(n) |
| result.sum += arr[i]; | n | O(n) |
| result.operations++; | n | O(n) |
| return result; | 1 | O(1) |
| TOTAL | 3n + 5 | O(n) |
|---|
ARRAY SUM - SPACE COMPLEXITY:
| Variable/Memory | Space Units | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| ArraySumResult result | 1 struct | O(1) |
| int i | 1 | O(1) |
| int arr[] (passed by ref) | 0 (no copy) | O(1) |
| int n | 1 | O(1) |
| TOTAL | 1 struct + 2 | O(1) |
|---|
LINEAR SEARCH - TIME COMPLEXITY:
| Statement | Best Case | Avg Case | Worst Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| LinearSearchResult result = {…}; | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| int i; | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| for (i = 0; i < n; i++) | 1 | n/2 | n+1 |
| result.comparisons++; | 1 | n/2 | n |
| if (arr[i] == target) | 1 | n/2 | n |
| result.found = true; | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| result.index = i; | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| return result; (found) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| return result; (not found) | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 8 | n+5 | 2n+5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMPLEXITY | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
| ------------------------------------ | ----------- | ---------- | ------------- |
LINEAR SEARCH - SPACE COMPLEXITY:
| Variable/Memory | Space Units | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| LinearSearchResult result | 1 struct | O(1) |
| int i | 1 | O(1) |
| int arr[] (passed by ref) | 0 (no copy) | O(1) |
| int n | 1 | O(1) |
| int target | 1 | O(1) |
| TOTAL | 1 struct + 3 | O(1) |
|---|
BUBBLE SORT - TIME COMPLEXITY:
| Statement | Best Case | Worst Case | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| BubbleSortResult result = {…}; | 1 | 1 | O(1) |
| int i; | 1 | 1 | O(1) |
| int j; | 1 | 1 | O(1) |
| int temp; | 1 | 1 | O(1) |
| for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++) | n | n | O(n) |
| for (j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) | n(n-1)/2 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| result.comparisons++; | n(n-1)/2 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) | n(n-1)/2 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| temp = arr[j]; | 0 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| arr[j] = arr[j+1]; | 0 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| arr[j+1] = temp; | 0 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| result.swaps++; | 0 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| return result; | 1 | 1 | O(1) |
| TOTAL COMPARISONS | n(n-1)/2 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL SWAPS | 0 | n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| ------------------------------------ | --------------- | --------------- | ------------ |
| SWAP OPERATIONS (3 per swap) | 0 | 3n(n-1)/2 | O(n²) |
| ------------------------------------ | --------------- | --------------- | ------------ |
| OVERALL COMPLEXITY | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(n²) |
| ------------------------------------ | --------------- | --------------- | ------------ |
Note: Even with optimizations, bubble sort is O(n²) due to nested loops
BUBBLE SORT - SPACE COMPLEXITY:
| Variable/Memory | Space Units | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| BubbleSortResult result | 1 struct | O(1) |
| int i | 1 | O(1) |
| int j | 1 | O(1) |
| int temp | 1 | O(1) |
| int arr[] (modified in-place) | 0 (no copy) | O(1) |
| int n | 1 | O(1) |
| int* sortedArray (pointer only) | 1 | O(1) |
| TOTAL | 1 struct + 5 | O(1) |
|---|